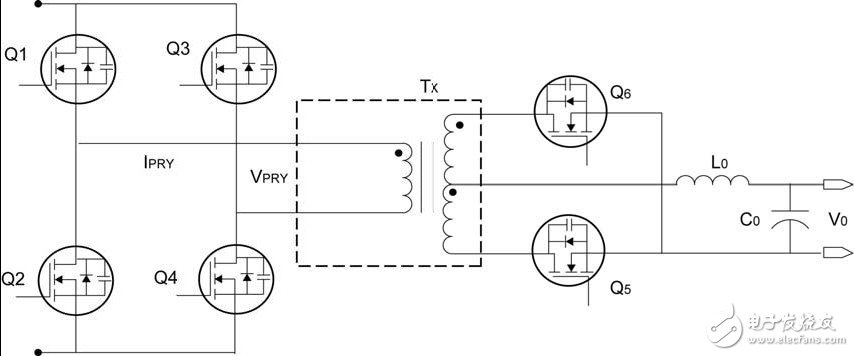
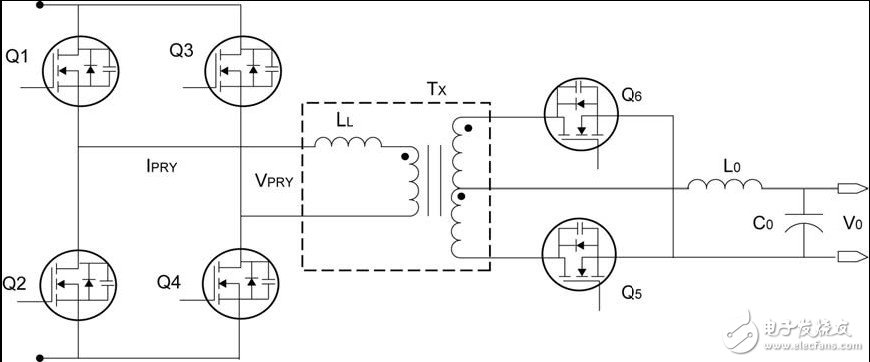
With the rise in energy prices and the successful implementation of various “environmental†programs, private companies and government regulators are increasingly demanding power supply manufacturers. The requirements of server power supplies have been further upgraded by the European Commission (the executive body of the European Union (EU)) and the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), which now covers efficiency at various load levels and standby power consumption. Server cluster operators have also made similar demands on power supply manufacturers. Because the regulations are so strict, and there are many regulations coming soon, power supply manufacturers are gradually turning to digital control. In an all-digital solution, a fully programmable Digital Signal Controller (DSC) directly generates PWM signals for controlling the power circuit stage. At the same time, the controller can handle system management tasks such as data logging, communication, and fault reporting. In this way, the power supply designer can write advanced control methods in the DSC, which is extremely difficult to achieve even in analog designs. Designers can use this feature to flexibly implement the data logging and communication standards required by end customers. The Phase-Shifted Full-Bridge (PSFB) topology is a DC-DC converter with the potential to meet future power efficiency requirements. The flexibility of the DSC makes the unstable PSFB topology easier to manage and enables advanced technologies that further increase PSFB efficiency. The inevitability of phase-shifted full-bridge topology Below we will discuss the simple full-bridge topology necessary for high-frequency operation and then discuss the efficiency improvement strategy. Full bridge converter As shown in Figure 1, the full-bridge converter is configured with four switches (Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4). When the diagonal switches Q1, Q4 and Q2, Q3 are turned on at the same time, a complete input voltage (VIN) is provided on the primary winding of the transformer. During each half cycle of the converter, the diagonal switches Q1 and Q4 or Q2 and Q3 are turned on and the polarity of the transformer is reversed every half cycle. In a full-bridge converter, the switching current and primary current at a given power will be halved compared to a half-bridge converter. This current reduction makes full bridge converters suitable for high power levels. However, diagonal switches use hard switches that cause high switching losses when turned on and off. In the past, power engineers had to use less efficient hard-switching power conversion methods because the right controllers had not yet appeared. The losses of these methods increase with increasing frequency, thus limiting the operating frequency, which in turn limits the ability of the power supply to supply power efficiently. Figure 1: Full Bridge Converter Soft Switch Full Bridge (PSFB) Topology With existing DSCs, designers can now consider using higher operating frequencies to reduce the number of magnetic and filter capacitors in the power supply. An increase in frequency can result in higher switching losses in hard switching power converters such as conventional full bridge converters. A better alternative is to choose a relatively complex soft switching method to reduce switching losses and provide higher power density. The PSFB converter is a soft-switching topology that uses parasitic capacitances (such as the output capacitance of switching devices such as MOSFETs and IGBTs) and the leakage inductance of the transformer to achieve resonant conversion. This resonant transition allows the switching device to have zero voltage across it when turned on, thereby eliminating switching losses when it is turned on. PSFB converters have been widely used in telecom and server applications where converter power density and frequency are critical. The general work of the PSFB converter is covered in many articles, and we will demonstrate how DSC can further improve performance. Figure 2: Phase-shifted full-bridge converter
Our abrasive discs have the good quality and competitive price in the market.Widely used in grinding and polishing process in the fields of iron and steel,building materials,ship aviation,vehicle,timber and plastic industries.
Aluminum oxide grain is used for polishing wood and soft metal.
Silicone carbide grain is used for polishing stone,plastic,fiberglass and concrete.
Calcined aluminum grain is used for polishing hard metal.
Zirconia grain grain is used for polishing stainless steel.
Abrasive Disc,Loop Grinding Disc,Film Disc For Automotive,Metal Grinding Disc Jiangsu Loncin Electric Equipment Co.,Ltd , https://www.loncincabletray.com