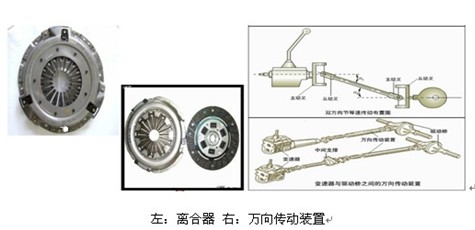
Foreword This article refers to the address: http:// The continuous development of electronic technology has promoted the upgrading of various products. For automotive electronics, its role is not to be underestimated. Automotive drive shafts (automotive drive shaft designs) are also being developed as part of the automotive drive train. So, what is the role of the car drive shaft? Xiaobian this article is to simply share the basic knowledge about the car drive shaft, understand the role of the car drive shaft (automobile sensor), to provide friends with automotive electronics research and development Reference and learning materials. The concept of automotive drive shafts (composition of automotive transmission systems) The original car was driven by a chain. In the 1940s, it was changed to a solid shaft drive shaft drive, and later changed to a hollow shaft. The engine and the drive shaft are longitudinally arranged, and the wheels are lateral, so the universal joints are mounted at both ends of the drive shaft. To understand the role of the car's drive shaft, let us first understand what is the car drive shaft. The automobile transmission shaft can transmit power between the two shafts of different axial centers and even between the two shafts whose relative positions are constantly changing during operation, and the circular object fittings which can be moved or rotated by connecting or assembling various accessories are generally light and Made of alloy steel pipe with good torsion resistance. For the front-engine rear-wheel drive car, the rotation of the transmission is transmitted to the main reducer shaft, which can be connected by a universal joint for several sections. The power of a typical automobile engine is transmitted to a drive wheel through a transmission, a drive shaft, a rear axle reducer differential, and the like. Since the drive shaft is mounted under the steel plate of the car, and the transmission is mounted on the frame (girders), the relative displacement of the leaf springs during the running is required, so the inclination angle of the drive shaft is often Changed. The bouncing of the steel plate continually changes the axis, the axial direction and the distance of the two parts of the transmission and the drive shaft. In this case, the transmission shaft and the telescopic joint are designed to ensure the transmission of torque. The role of the car drive shaft The universal joint transmission device is composed of a universal joint, a transmission shaft and an intermediate support. When the distance is long, a segmented drive shaft is required, and an intermediate support is added in the middle. When the car is turning or encountering uneven road surface, in order to ensure that the power is still transmitted, a device capable of changing the angle is required to transmit power, and the universal joint device is born. Its main function is to connect the transmission output shaft and the final drive input shaft that are not on the same line, and to ensure reliable transmission of power when the angle and distance between the two shafts are constantly changing. It is similar to the part of the arm that still has the wrist, which can transmit power and realize all the actions of the car. The drive shaft and the universal joint are mainly used to transmit the torque, so that the car is not restricted by the up and down movement of the rear drive axle during operation. They are usually mounted between the transmission and the rear axle drive shaft. According to different models and transmission modes, the number of transmission shafts and universal joints is different. Generally, medium-sized trucks are two transmission shafts, three sets of universal joints and one set of expansion joints. Torque deformation means that the rods are subjected to force couples of equal magnitude, opposite directions and acting plane perpendicular to the axis of the rod, such that the cross-section of the rod rotates about the axis. Torsional deformation members are typically shaft-like parts that are generally circular in cross-section. The joints of the main and driven shafts whose angular velocity is still equal when the angle between the two axes changes are called constant velocity joints or equal angular joints. They are mainly used in the wheel drive of steering axles, disconnected drive axles, de Doin drive axles, mainly for power transmission in cars. When the car is driven by the rear wheel, the cross shaft universal joint drive shaft is often used; when the car is driven by the front wheel, the constant velocity joint is often used - the constant velocity joint is also a drive shaft, just the title Different. At present, the cross-shaft rigid universal joint drive shaft is the most widely used in the automotive transmission system. Another important component is the sliding spline pair, which consists of internal and external splines for transmitting length changes. The universal joint swing angle of the drive shaft and the maximum expansion and contraction amount of the sliding spline pair are determined according to the drive shaft runout check performed during the entire vehicle arrangement. In general, there may be a drive shaft tube. The hollow shaft tube has a small mass but can transmit a large torque and has a higher critical speed than a solid shaft of the same outer diameter. In general, the role of the automotive drive shaft is to transfer power between the two axes of different axes, even between the two axes whose relative positions are constantly changing during operation. Classification of automotive drive shafts According to different classification methods, the automobile transmission shaft can be divided into open and closed, open living in a bare environment, and closed living in a closed environment. Due to the features of installation, maintenance and maintenance, the open drive shaft is widely used. There are different classifications depending on the gimbal, an important part of the drive shaft itself. If the universal joint has obvious elasticity in the direction of twisting, it can be divided into a rigid universal joint drive shaft and a flexible universal joint drive shaft. The former relies on the hinged connection of the parts to transmit power, while the latter relies on elastic parts to transmit power and has a buffer damping effect. Rigid joints can be divided into non-equal joints (such as cross-shaft universal joints), quasi-constant joints (such as double joints, three-pin joints) and constant speed. Universal joints (such as ball cage joints, ball fork joints). The constant velocity and the unequal speed refer to whether the angular velocity of the driven shaft is uniform during the week when the driven shaft rotates. Of course, the average rotational speeds of the driven shaft and the driven shaft are equal. to sum up The chassis electronics of the car is mainly composed of the drive train, the driving system, the steering system and the brake system. The drive train is mainly embodied in the mechanical mechanism. It has some mechanical products to form and realize the function of the vehicle power transmission. The concept and characteristics of the automobile transmission shaft are mainly introduced in detail. Skiving through mechanical action, the long strip plate cuts the material out of sheets and straightens at a certain angle, and repeatedly cuts to form a uniform clearance structure. It is used to solve the heat dissipation of high power devices under the condition of air cooling and heat dissipation, which can improve the heat dissipation efficiency by 8 ≤ 15% compared with the insert heatsink. Skived Fin,Skiving Process,Skiving Fin Heatsink,Gear Skiving Process Dongguan Formal Precision Metal Parts Co,. Ltd , https://www.formalmetal.com